AWS IAM: Getting Started, Best Practices, and More
Table of Contents
What is AWS IAM?
AWS IAM is a service that allows you to control access to AWS resources. It lets you create and manage users, groups, and roles and assign specific permissions to them. This ensures that only authorized individuals can access your AWS resources and perform specific actions. You can create and manage identities for your employees and applications using IAM, and you can give each one a different level of access.
In this article, we will use a scenario to explore the core concepts of AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) and provide a step-by-step guide on how to set them up in the AWS Management Console. IAM is important in managing access to your AWS resources and ensuring the security and compliance of your infrastructure.
Let’s get started!
Key Concepts in AWS IAM: Users, Groups, Roles, and Policies
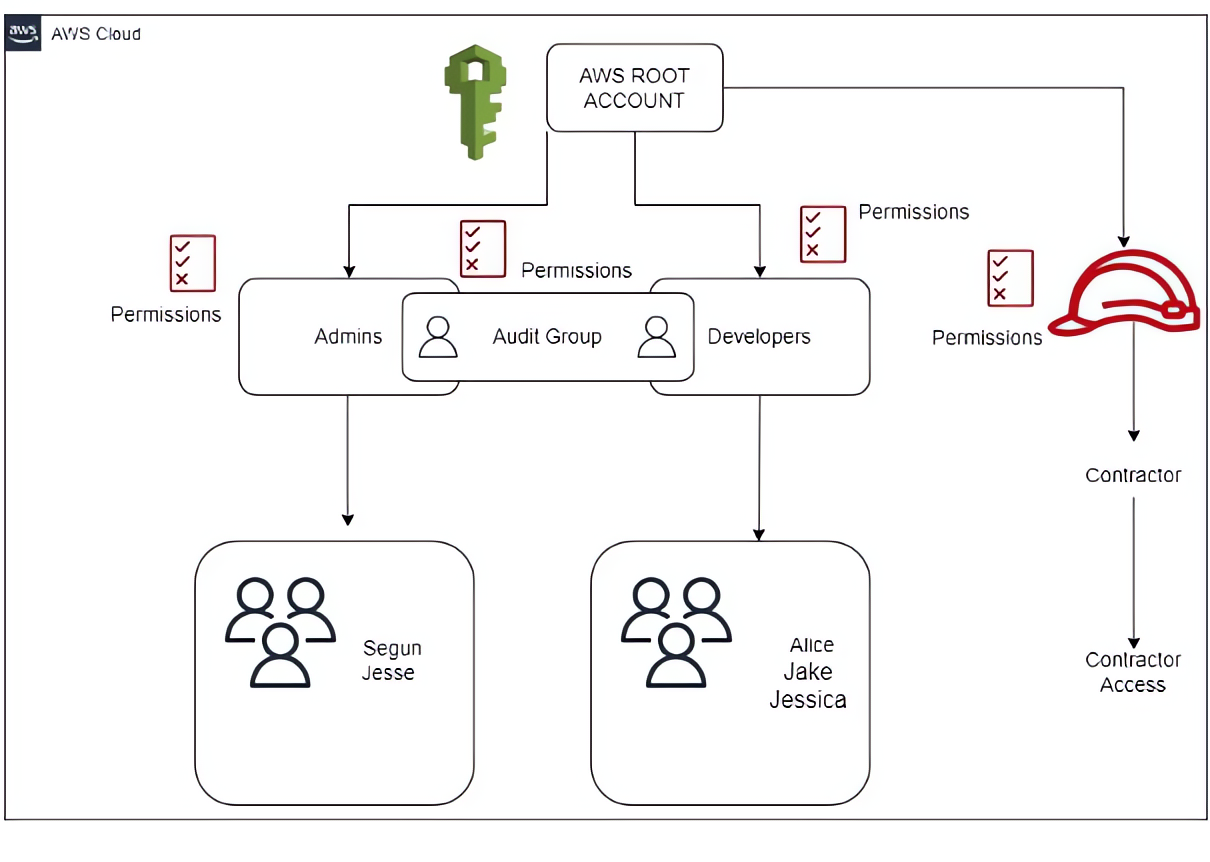
To understand the core concepts of IAM, let’s imagine you work for a company that hosts web applications on AWS. The company’s current AWS IAM setup is becoming increasingly complex and challenging to handle. The existing system lacks centralized management, and can’t handle growing numbers of users and a diverse set of applications that needs a unique set of permissions, leading to difficulties in managing permissions for team members effectively. This scenario requires the need for an efficient and resilient solution to simplify the access management processes and enhance security within our AWS environment. Your team is in charge of managing access to these applications and their resources. By leveraging IAM, you can effectively control permissions and enhance security.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this step-by-step tutorial, you should have the following:
An AWS account: You need to have an AWS account to create the IAM user. On any browser of your choice, you can navigate to the AWS sign-up page using this link (AWS portal).
To enable multi-factor authentication (MFA), you must have an MFA device that is compatible with AWS. AWS supports virtual MFA devices, hardware MFA devices, and SMS text message MFA. In this guide, you will make use of virtual devices like Microsoft Authenticator, which you can download from the App Store on your phone.
Step 1: Creating IAM Groups
What is AWS IAM Group?
With the IAM group, you can categorize users and define their permissions. Think of it as a collection of users that have similar access needs. For example, you have an IAM group for your development team that has access to specific AWS resources, like EC2 instances.
By creating IAM groups, you can easily manage permissions for multiple users all at once. Instead of assigning permissions to each user, you can assign them to a group, and all users in that group inherit those permissions. This saves you time and helps maintain consistent permissions across your organization. You can also nest IAM groups within each other. This means you can have a group that contains other groups, allowing you to easily manage complex permission structures.
The first step to setting this up is to create IAM groups to categorize users based on their access needs. We’ll create three groups: an “Admins” group for team members who require administrative access to the web application, the “Developers” group for those who only need access to development resources, and lastly an “Audit” group for members of this group that requires both administrative and development access.
Sign into the AWS Management console and in the search bar, type in IAM and click on “IAM” from the search results to navigate to the IAM console

Click on “User groups” on the left-hand menu of your screen, and click on the “Create group” button.
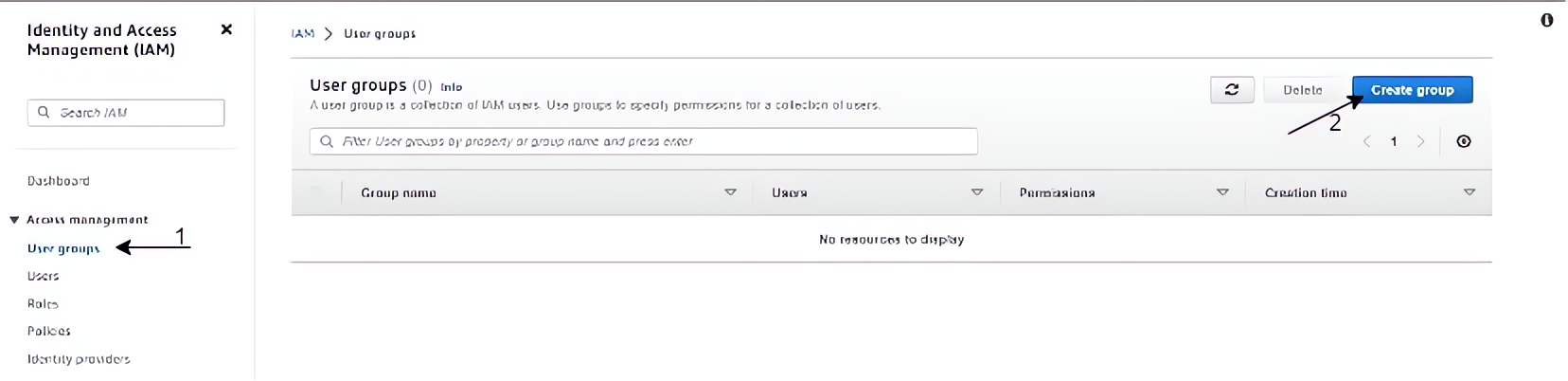
Name this group as “Admin” and create it, repeat the previous step with this step to create groups for “Developers” and “Audit”.
Step 2: Creating IAM Policies
What is an AWS IAM Policy?
AWS IAM policies are rules that explain actions that can be taken on AWS resources and who is allowed to take those actions. They are used to grant or deny permissions to users, groups, and roles in AWS. IAM policies are attached to users, groups, and roles, allowing you to control access to AWS resources based on your specific requirements.
IAM policies are written in JSON format, which makes them easy to read and understand. An IAM policy includes a list of statements, each of which contains a condition and an effect. The condition specifies which actions the policy applies to, and the effect specifies whether those actions are allowed or denied.
List permissions allow users to view a list of resources without being able to view or modify the details of individual resources, to view the details of individual resources use read permissions. Write permissions allow users to make changes or modifications to resources
There are two types of IAM policies: managed policies and inline policies.
Managed policies are independent policies that are attached to multiple users, groups, and roles. They are created and managed separately from the entities they are attached to. Inline policies are policies created and attached to a single user, group, or role. They are managed in line with the entity they are attached to.
Next, we’ll create IAM policies that define the permissions for each group. For the “Admins” group, we’ll create a policy that grants administrative access to the web application, another for the “Developers” group, which grants access to development resources, likewise with the Audit group and for the Contractor role.
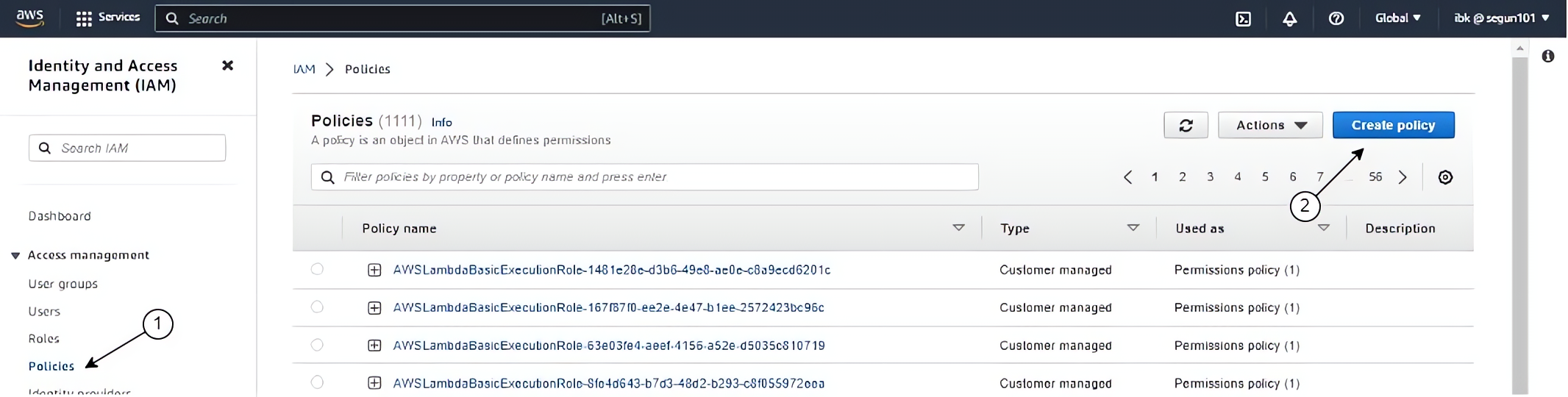
Click on “Policies” on the left-hand menu of your screen, and click on the “Create policy” button.
In the search bar, type in “AdministratorAccess” click on it to copy the permission in JSON format for the Admin team
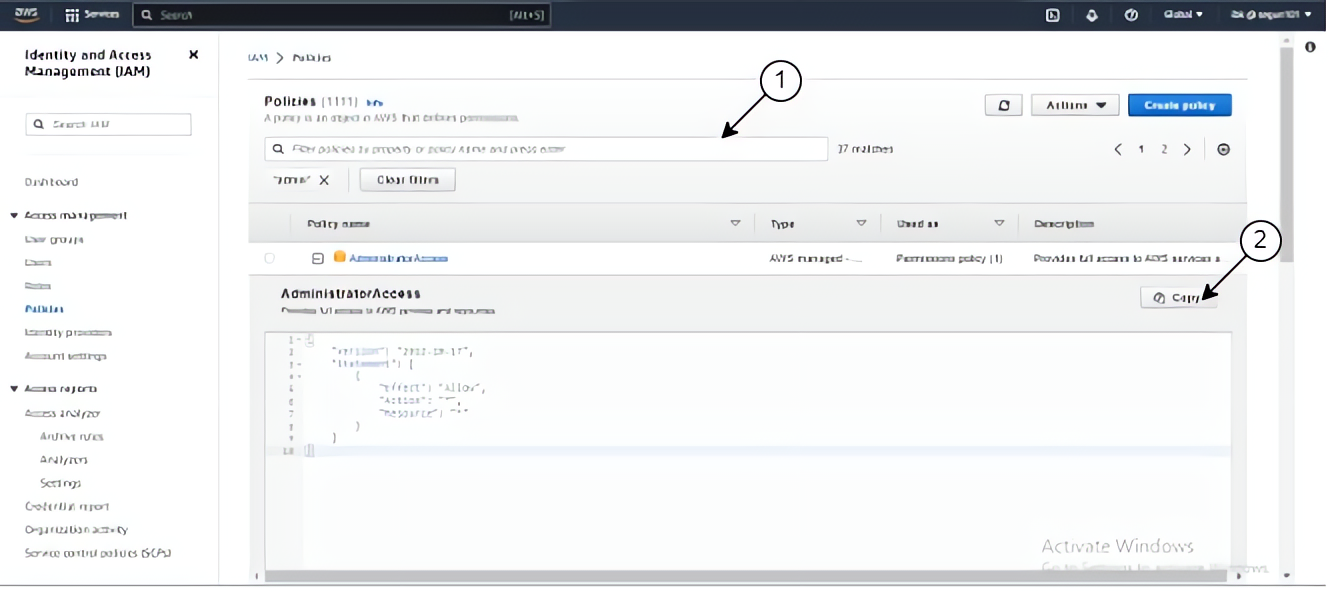
Click on the JSON button, to open the policy editor and paste the JSON code
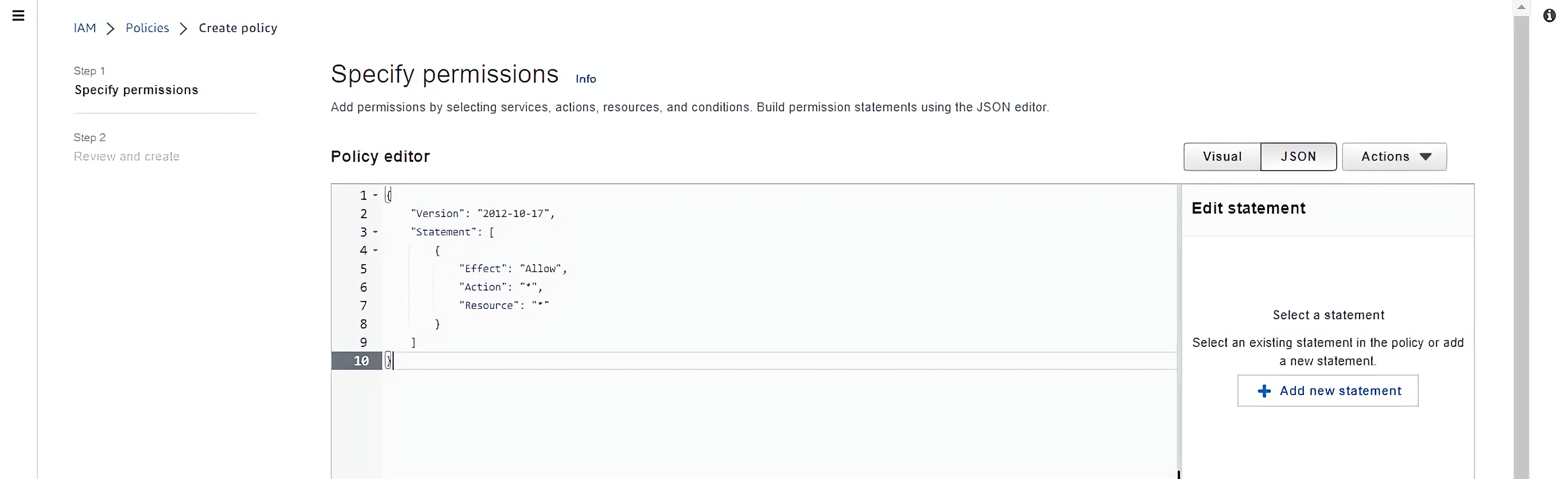
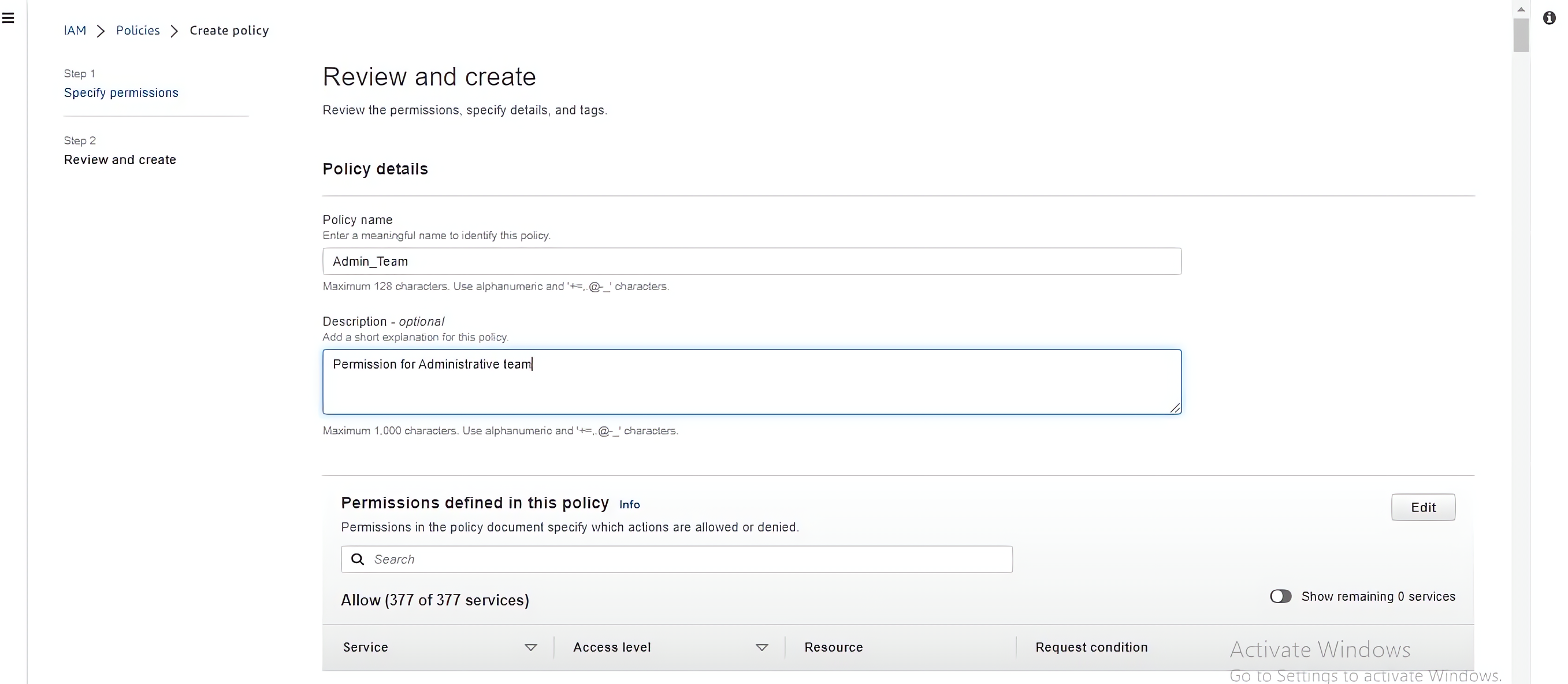
Write the specified name of the policy and the description of the policy (Administration team giving Administrative access) and click on create policy
Specify permissions for the Development team by using the search bar to search for services used in development like EC2 instances and CodeCommit.
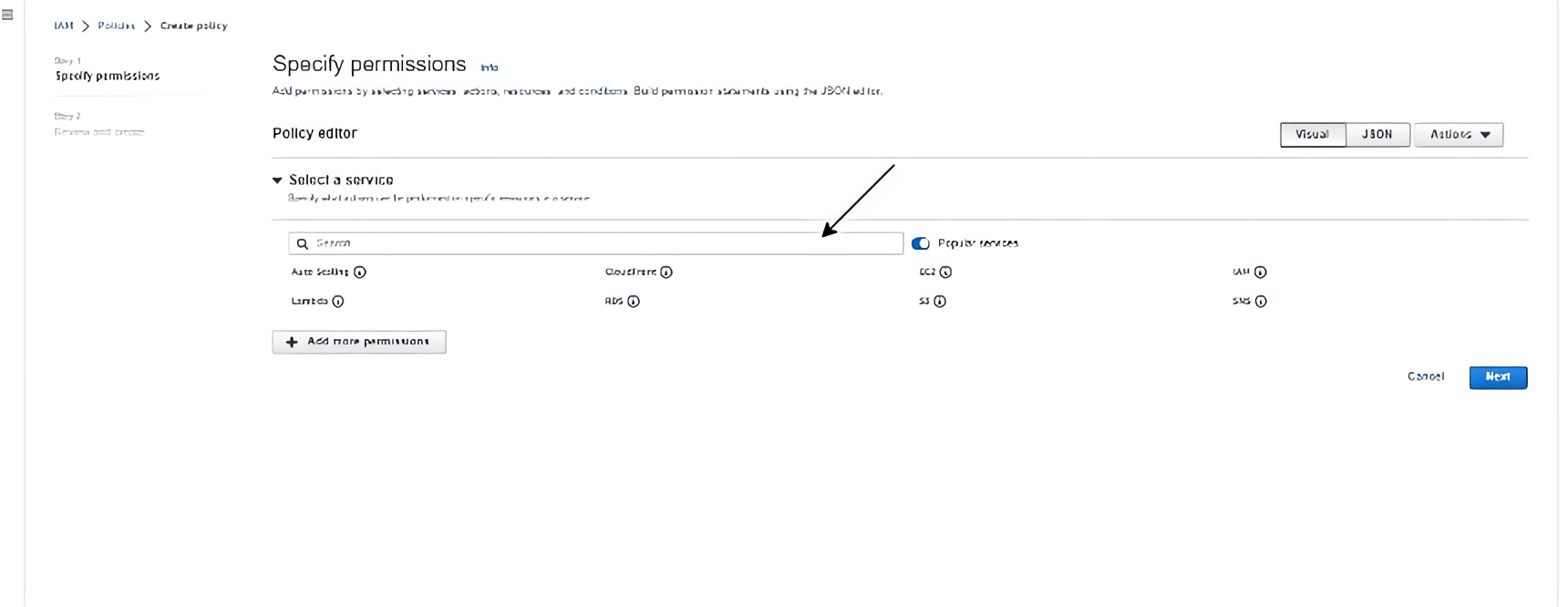
At this stage, you have selected the EC2 service, specify actions from the service to be allowed.
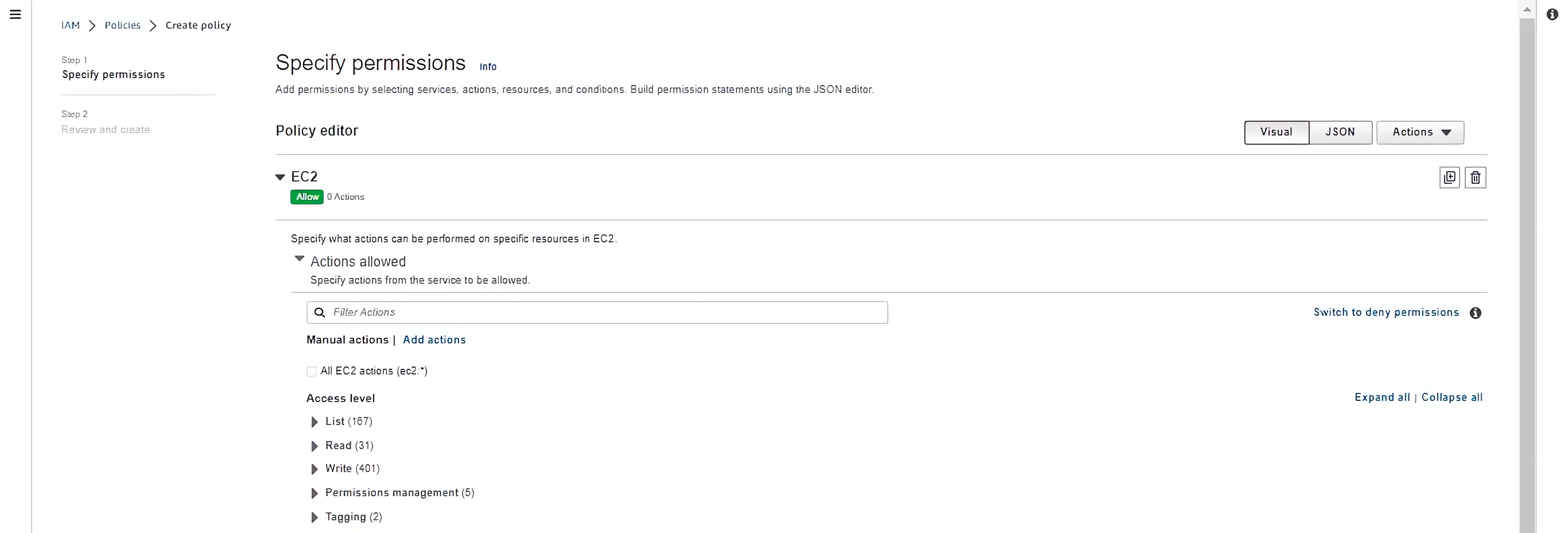
Choose actions that will let you start, run and terminates EC2 instances and pull and push code with CodeCommit:
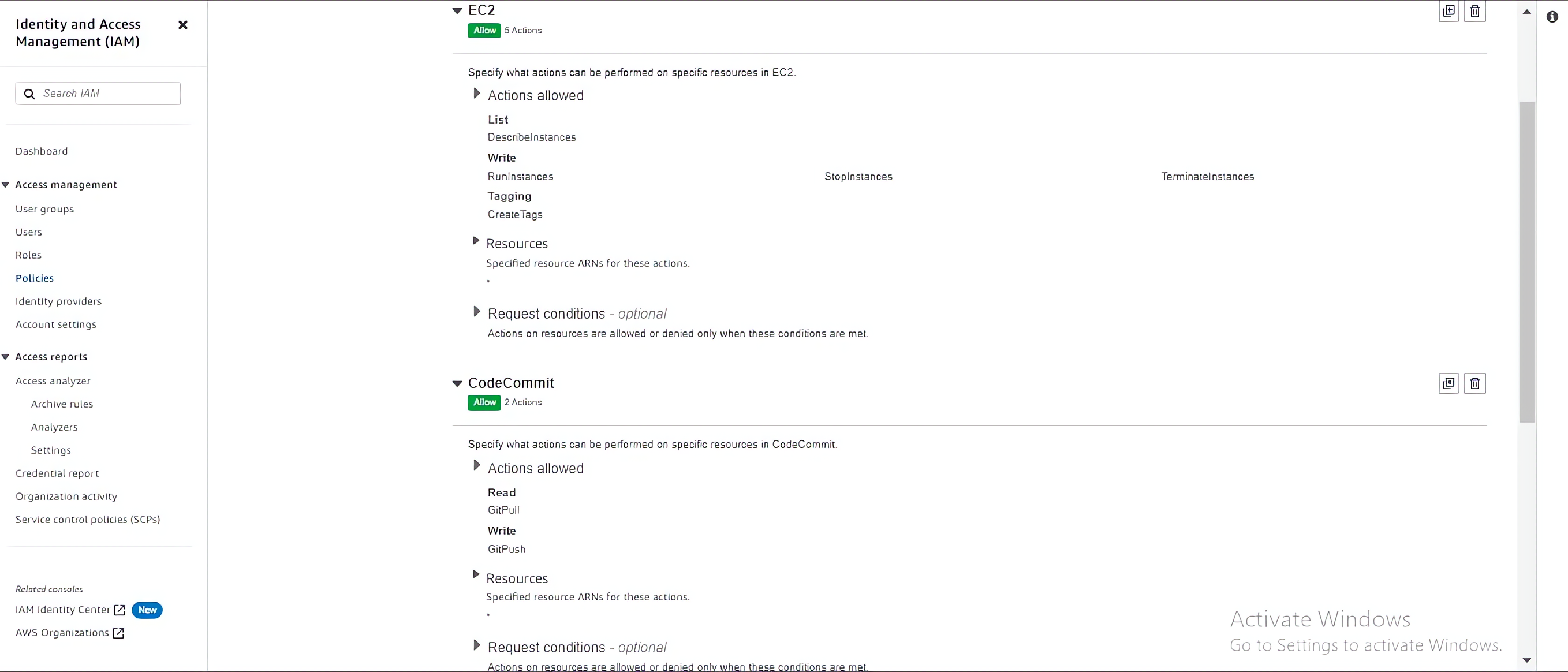
To specify the permission for the Audit group, you can also use the visual editor to select services like CloudWatch that will be needed by the Audit team:
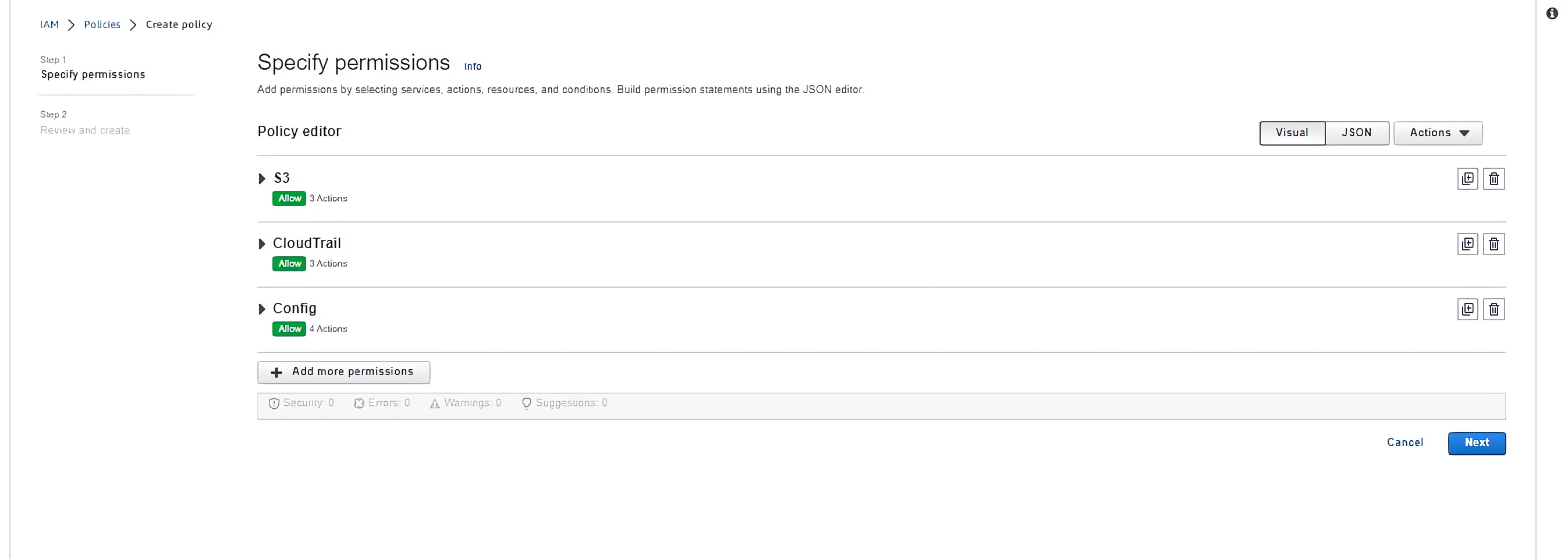
Step 3: Creating and adding IAM Users to Groups
What is an AWS IAM user?
An IAM user is an entity that represents a person or an application that communicates with AWS. You can restrict a user’s access to AWS resources by giving them specific rights. For example, you can give a user permission to read data from an S3 bucket but not delete it.
Each user has their own set of credentials, which are a username and password, or access key, used to authorize access to AWS resources. With IAM users, it’s easy to withdraw access for a specific user if their access is no longer needed or if their credentials have been compromised. This helps ensure your AWS resources are secured.
When To Use The Root User?
The user created the first time you open an AWS account is called the root user. It is important to note that the root user should not be used for routine tasks except for initial account setup due to the elevated privileges it has and the potential risks involved with using it.
It’s best practice to create and use an IAM user with the appropriate rights for everyday tasks. The possibility of harmful actions being committed on your AWS resources is reduced due to the ability to create IAM users with restricted access based on the operations the user needs to complete.
Best Practices for Creating Users
There are recommended practices you should adhere to when creating AWS IAM users to guarantee security, manageability, and compliance.
Access key management: To reduce the risk of illegal access, use access keys only when necessary, and rotate them regularly.
Password policies: Implement a strict password policy for your IAM users to protect the security of their login credentials. This includes but is not limited to establishing password length requirements and enforcing the use of special characters. Naming policies: For better access control administration and management, it is recommended to use names that describe the role or function of users.
After defining the groups and policies, we’ll create IAM users and add them to the respective groups. For example, we’ll create users named “Jesse” and “Segun” and add them to the “Admins” group. They will automatically inherit the administrative permissions defined in the associated policy. Similarly, you create users named “Alice,” “Jake,” and “Jessica” and add them to the “Developers” group, granting them the necessary access for their roles.
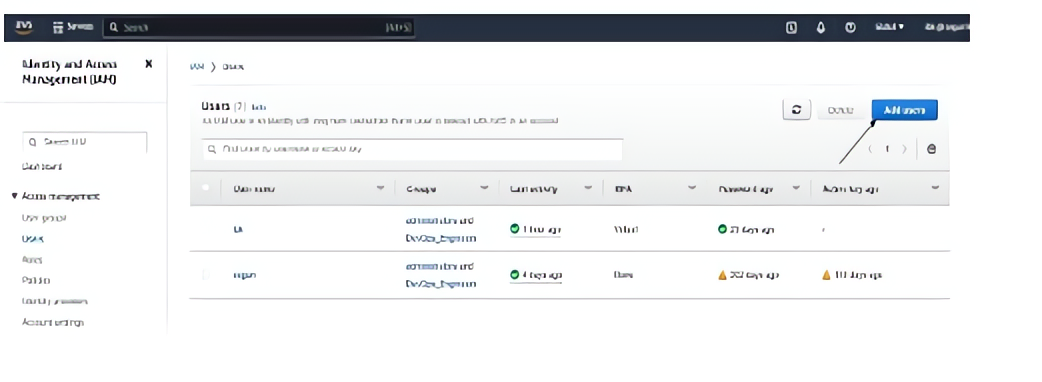
On the IAM dashboard, click on “Users” on the left-hand menu of your screen:
After clicking on “Users”, click on the “Add users” button on the dashboard:
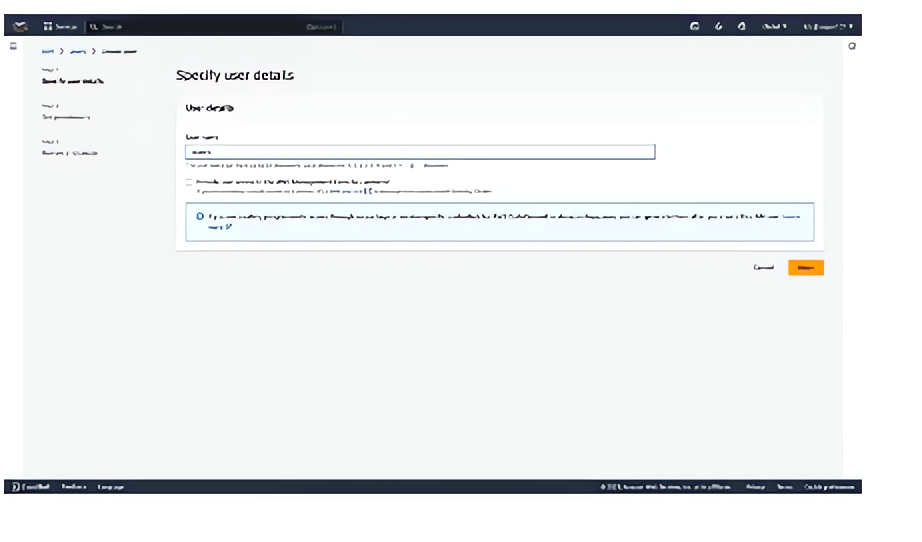
Specifying user details
Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
To increase the security of your AWS account, enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all IAM users. In the scenario that an IAM user’s credentials are stolen, having MFA enabled will prevent unwanted access to your resources.
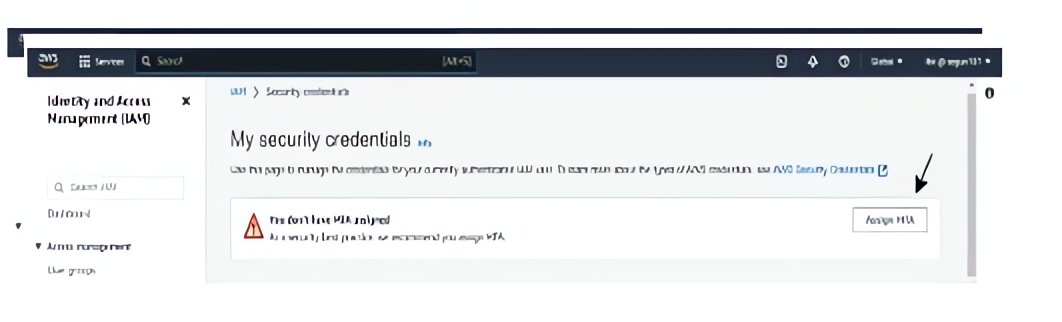
To set up Multi- Factor Authentication (MFA) Click the IAM user you just created to enable MFA
Click on the “Security credentials” tab for the selected user.
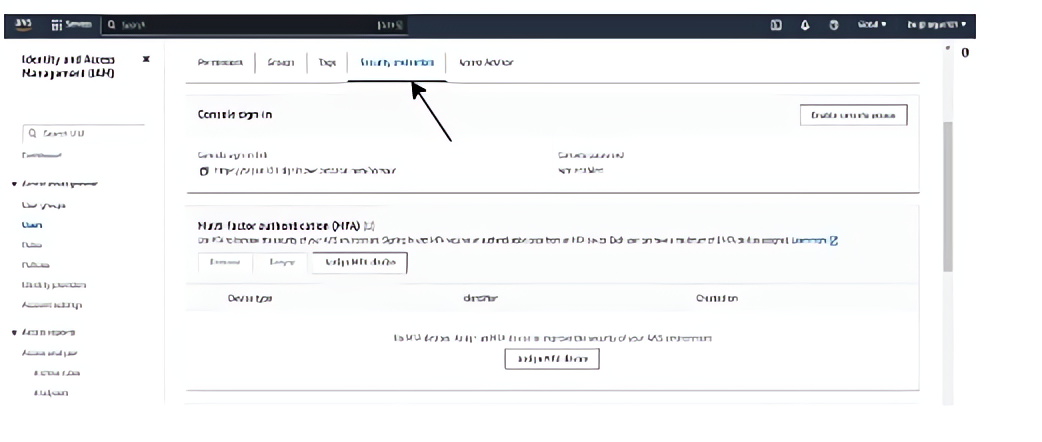
Click on the “Assign MFA” button.
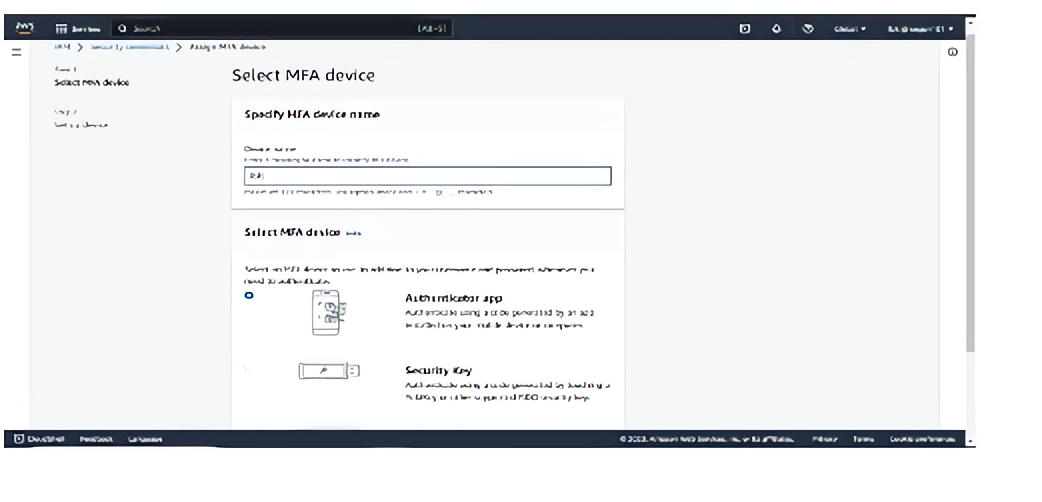
Select the Authenticator app option ( i.e Microsoft Authenticator or any authenticator app of your choice). Follow the steps on your screen, open your authenticator app and scan the QR code.
To complete configuration, click the “Add MFA” button.

Step 4: Granting Temporary Access with IAM Roles
What is AWS IAM role? IAM roles are a way to grant temporary permissions to an AWS resource, such as an S3 bucket. Rather than assigning permissions to a user, you assign them to a role, which can be assumed by a trusted entity.
Roles give you a secure way to assign permissions without exposing access keys, which can eventually be a security risk. For example, you create a role that allows access to specific S3 buckets and then assign that role to an EC2 instance. When the instance needs to access the S3 bucket, it will assume the role and use the temporary permissions to perform those actions.
Roles can also be used to transfer permissions across accounts. For example, you have separate AWS accounts that contain your production resources and development resources. You can create a role in your production account that grants access to specific resources and then allow users in your development account to assume that role. With this, users in your development account can access those production resources without requiring direct access to the entire production account.
One of the benefits of using IAM roles is that they are highly flexible. You can customize the permissions granted by a role based on the requirements of the trusted entity. You can also modify or revoke permissions by updating roles at any time.
Finally, you also need to grant temporary access to AWS resources to an external contractor who is helping with some development work. To do this, you create an IAM role called “ContractorAccess” and define a custom IAM policy that specifies the resources and permissions that the contractor will need access to. You provide the contractor with the necessary permissions by allowing them to assume the “ContractorAccess Role”.
On the IAM console, click on “Roles” in the left navigation pane. Click on the “Create role” button.
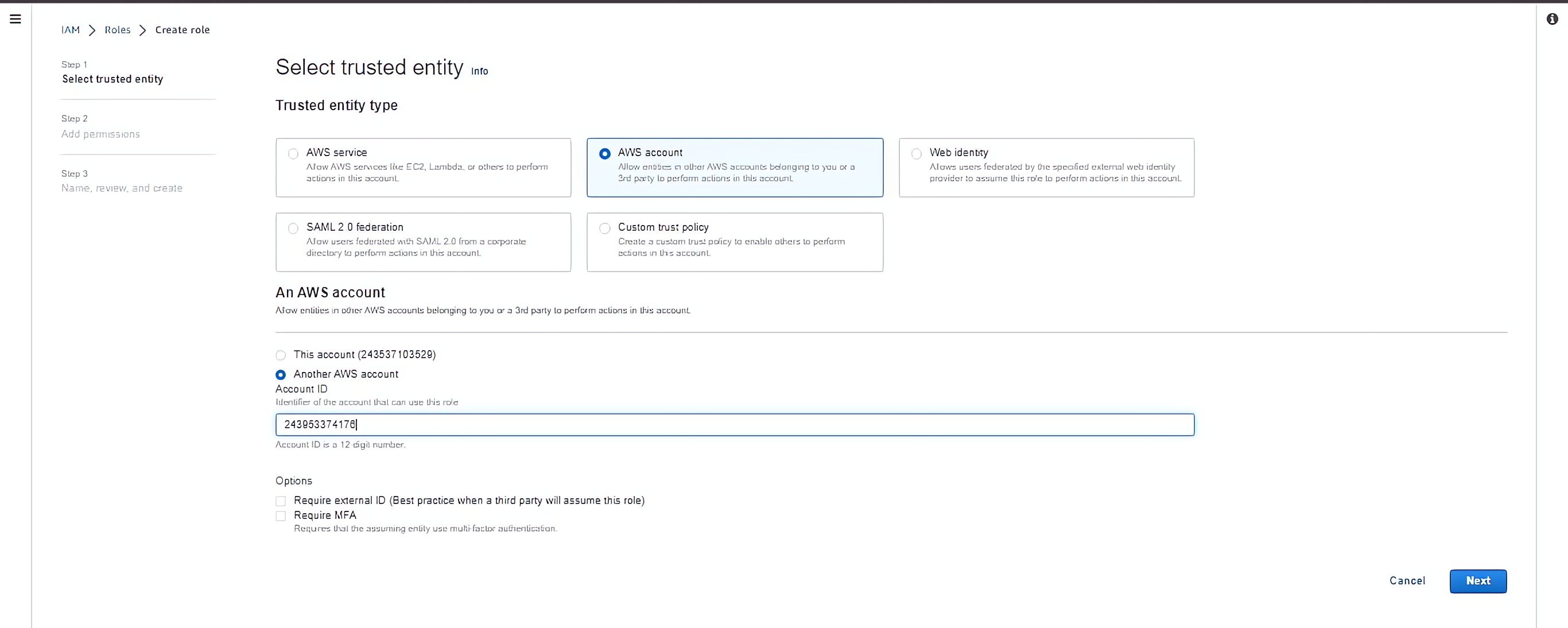
In the “Select type of trusted entity” section, choose “Another AWS account” as the trusted entity. Enter the AWS account ID of the contractor’s account in the “Account ID” field.
Click on the “Next” button, click on the “Create policy” button to define a custom IAM policy for the contractor.
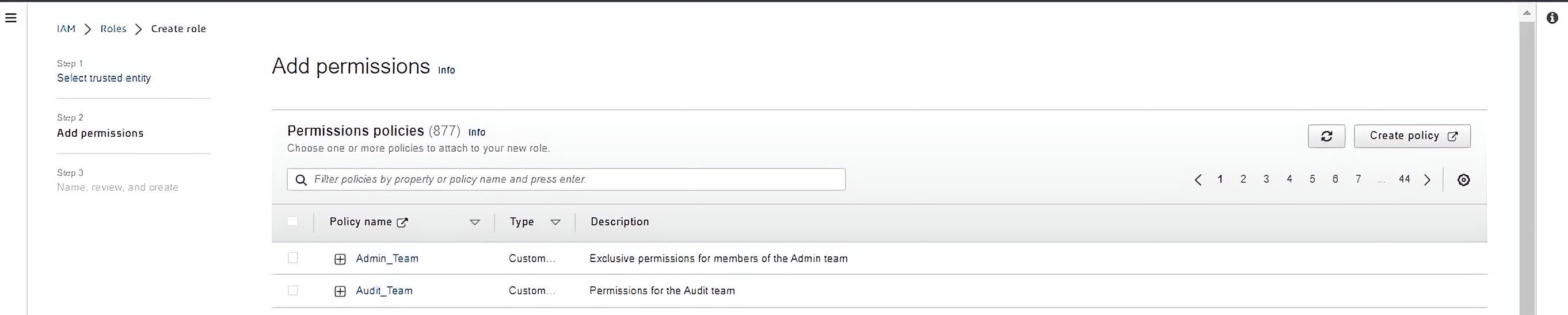
Select the appropriate services, e.g S3, SNS etc and actions that the contractor needs access to. Review the policy and click on the “Create policy” button to save it.
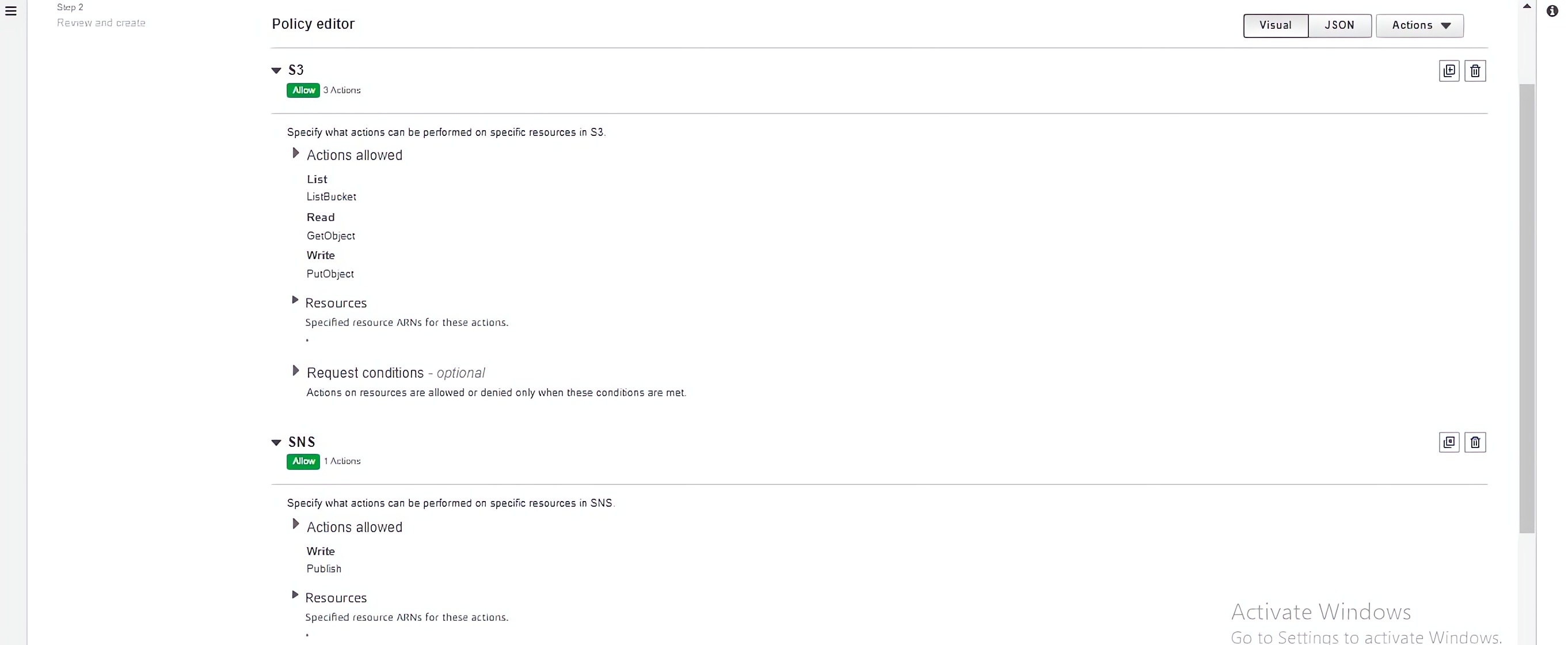
Return to the role creation wizard to view the newly created policy. Select the policy and click on the “Next” button on your screen
Provide a name for the role (e.g., “ContractorAccess”) and an optional description. Click on the “Create role” button to create the IAM role.
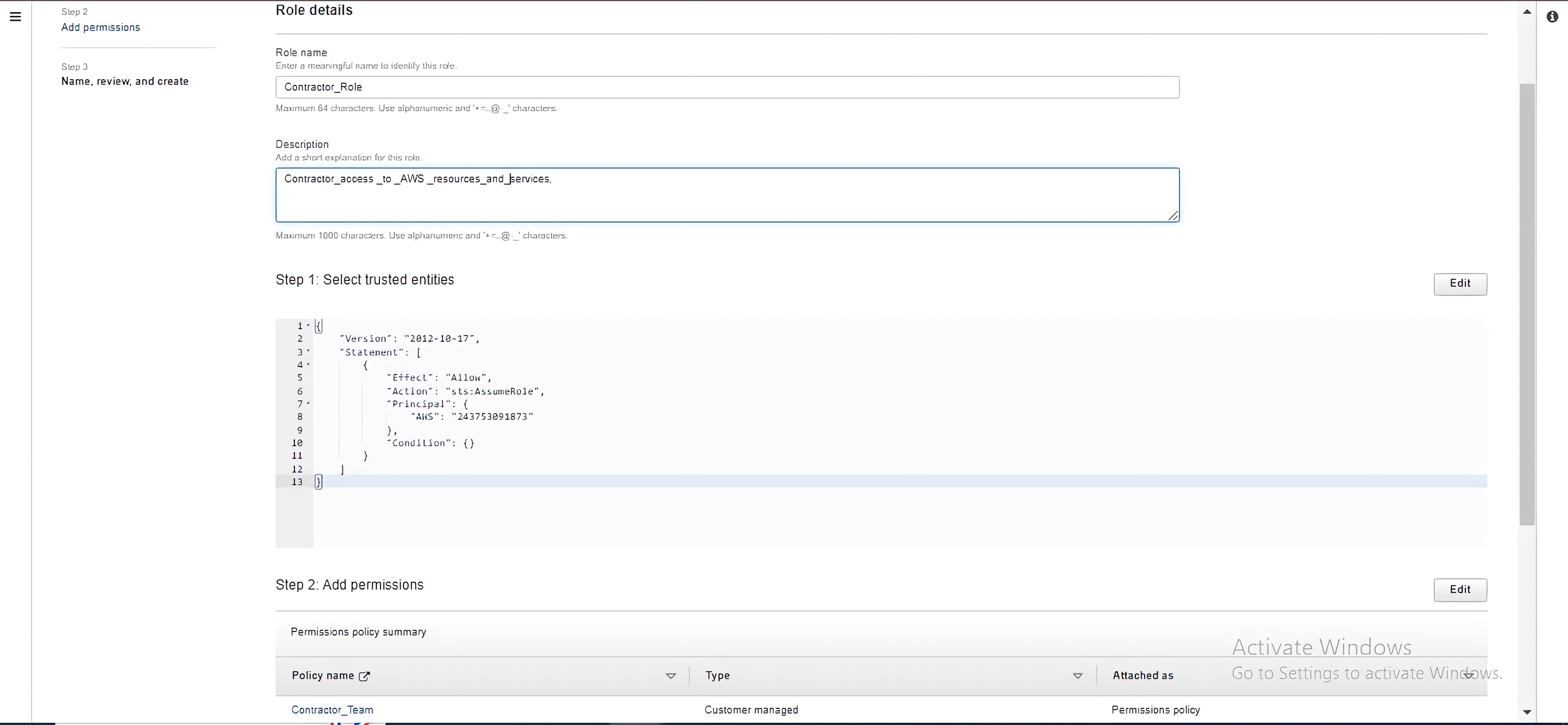
AWS IAM policies, groups, users, and roles work together to manage permissions and access control for AWS resources. By using these components effectively, you can manage access to AWS resources securely and efficiently.
Monitoring IAM Activity Logs
The integrity, and security of your AWS environment, need to be monitored regularly through your IAM activity logs. You can track who is using your resources and what they are doing by monitoring their IAM activity. These logs work as an essential detective tool, allowing you to quickly see any malicious behavior.
You can see trends, patterns, or potential security breaches with efficient IAM log monitoring. You can get in-depth audit logs that track IAM actions, such as user sign-ins, policy changes, permission adjustments, and more, by using AWS services like CloudTrail. You can also find hostile insider behavior and account breaches by analyzing these logs.
AWS Config is a great tool that lets you assess, analyze, and audit the configurations of your AWS resources. You can create rules for your AWS resources and ensure they adhere to your security requirements by using AWS Config rules. With these rules, your configurations in your IAM resources (user accounts, groups, and policies), can be tracked.
Third-party tools can also be used to audit and enforce best practices in AWS IAM. These tools can help you monitor and analyze your IAM resources to detect any vulnerabilities or misconfigurations. Some of the popular third-party tools used for IAM security include Auth0, Okta, and OneLogin.
It’s important to regularly audit and enforce best practices using tools like AWS Config Rules and third-party tools. By doing this, you can easily identify and resolve any possible vulnerabilities or misconfigurations, which can help prevent security breaches and protect your company’s sensitive data.
It’s important to be wary of any potential threats to security and take the necessary precautions to address them. Here are some recommendations for securing your IAM credentials:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) should be enabled for all users, and strong password policies should be put in place.
When possible, replace IAM roles for IAM users. IAM roles offer temporary credentials and are less vulnerable to credential abuse and theft.
IAM resources should only be accessible to groups and users with permission. By doing this, you can be sure that only authorized users may access your AWS resources.
Change the IAM access keys regularly. By doing this, the possibility of key compromise and unauthorized access will be reduced.
All IAM activities should be tracked and recorded using AWS CloudTrail. Use this to identify any unauthorized changes to your IAM configuration.
AWS offers several tools, such as AWS Config Rules and third-party tools, to assist you in achieving a secure environment while following best practices.
Conclusion
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is your handy tool to effectively control access to your AWS services. You can maintain security and manage user permissions by adhering to AWS best practices.
We looked at the fundamentals of IAM through this article, including steps in creating IAM users, groups, and roles, as well as how to use IAM policies to apply fine-grained permissions. We also stressed the importance of multi-factor authentication (MFA) in improving the security of your AWS accounts.
Also in this article, the significance of continuing IAM management was highlighted. IAM rules should be regularly reviewed to ensure that permissions adhere to the least privilege principle and also be updated concerning changes in your company’s demands. You can also track any unusual behavior, address any security concerns, and maintain the integrity of your AWS environment by keeping a keen eye on your IAM activity logs.
Turn your engineering standards into automated guardrails that provide feedback directly in pull requests, with 100+ guardrails included out of the box and support for the tools and CI/CD systems you already have.



